Hello Its Us The Techs Tips Hapy New Year For First.
:)
Now For This New Year We AreGona Show To You All HTML Docs Tuto Of What We POst Here In Our Blog
We Will Start With The BAsicis
NOTE:YOU GOT TO PRESS CTRL + U TO WIEV THE CODE IN OUR TUTOS PAGE OR RIGHT CLICK AND SELECT WIEVS THE PAGE SOURCE OK!
THE FIRST IS THE TITLE NAME OF THE HTML DOC:
http://pastehtml.com/raw/cnqsxb77q.html
------------------------------------------------------------------
HTML LINKS
http://pastehtml.com/raw/cnqv38uau.rtxt
-------------------------------------------------------------------
TEXT FORMATING
http://pastehtml.com/raw/cnr0k53rq.html
-------------------------------------------------------------------
HTML IMAGE
http://pastehtml.com/raw/cnr1j7jau.html
AND THIS IS ALL FOR THIS TIME LEARN THIS AND MAKE DEMO HTMLS
FOR HELP
http://the-techs-tips.blogspot.com/2012/12/what-is-html-html5-xhtml.html
http://the-techs-tips.blogspot.com/2012/12/how-to-create-html-file.html
The Techs Tips
WEB DEVELOPMENT WEBSITE NOTE YOU GOT TO WAIT 5 SEC AND CLICK THE YELLOW BUTTON SKIP TO CONTINUE TO WEBSITE :)
Wednesday, January 2, 2013
Wednesday, December 26, 2012
Three Ways to Insert CSS
There are three ways of inserting a style sheet:
External style sheet
Internal style sheet
Inline style
External Style Sheet
An external style sheet is ideal when the style is applied to many pages. With an external style sheet, you can change the look of an entire Web site by changing one file. Each page must link to the style sheet using the <link> tag. The <link> tag goes inside the head section:
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css">
</head>
An external style sheet can be written in any text editor. The file should not contain any html tags. Your style sheet should be saved with a .css extension. An example of a style sheet file is shown below:
hr {color:sienna;}
p {margin-left:20px;}
body {background-image:url("images/back40.gif");}
Do not add a space between the property value and the unit (such as margin-left:20 px). The correct way is: margin-left:20px
Internal Style Sheet
An internal style sheet should be used when a single document has a unique style. You define internal styles in the head section of an HTML page, by using the <style> tag, like this:
<head>
<style>
hr {color:sienna;}
p {margin-left:20px;}
body {background-image:url("images/back40.gif");}
</style>
</head>
Inline Styles
An inline style loses many of the advantages of style sheets by mixing content with presentation. Use this method sparingly!
To use inline styles you use the style attribute in the relevant tag. The style attribute can contain any CSS property. The example shows how to change the color and the left margin of a paragraph:
<p style="color:sienna;margin-left:20px">This is a paragraph.</p>
Multiple Style Sheets
If some properties have been set for the same selector in different style sheets, the values will be inherited from the more specific style sheet.
For example, an external style sheet has these properties for the h3 selector:
h3
{
color:red;
text-align:left;
font-size:8pt;
}
And an internal style sheet has these properties for the h3 selector:
h3
{
text-align:right;
font-size:20pt;
}
If the page with the internal style sheet also links to the external style sheet the properties for h3 will be:
color:red;
text-align:right;
font-size:20pt;
The color is inherited from the external style sheet and the text-alignment and the font-size is replaced by the internal style sheet.
CSS Id and Class
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.center
{
text-align:center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="center">Center-aligned heading</h1>
<p class="center">Center-aligned paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
ANOTHER EXAMPLE
<html>
<head>
<style>
#para1
{
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="para1">Hello World!</p>
<p>This paragraph is not affected by the style.</p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p.center
{
text-align:center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="center">This heading will not be affected</h1>
<p class="center">This paragraph will be center-aligned.</p>
</body>
</html>
CSS Syntax
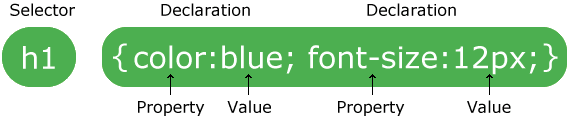
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p
{
color:red;
text-align:center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello World!</p>
<p>This paragraph is styled with CSS.</p>
</body>
</html>
CSS Introduction
What is CSS?
- CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
- Styles define how to display HTML elements
- Styles were added to HTML 4.0 to solve a problem
- External Style Sheets can save a lot of work
- External Style Sheets are stored in CSS file
Thursday, December 20, 2012
DRAG AND DROP IMAGES IN HTML5
THE FIRST TUTORIAL I HTML5
THE CODE
WHAT IS HTML5
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
#div1 {width:350px;height:70px;padding:10px;border:1px solid #aaaaaa;}
</style>
<script>
function allowDrop(ev)
{
ev.preventDefault();
}
function drag(ev)
{
ev.dataTransfer.setData("Text",ev.target.id);
}
function drop(ev)
{
ev.preventDefault();
var data=ev.dataTransfer.getData("Text");
ev.target.appendChild(document.getElementById(data));
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Drag the W3Schools image into the rectangle:</p>
<div id="div1" ondrop="drop(event)" ondragover="allowDrop(event)"></div>
<br>
<img id="drag1" src="http://i47.tinypic.com/165s8x.jpg" draggable="true" ondragstart="drag(event)" width="336" height="69">
</body>
</html>
THE CODE
WHAT IS HTML5
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
#div1 {width:350px;height:70px;padding:10px;border:1px solid #aaaaaa;}
</style>
<script>
function allowDrop(ev)
{
ev.preventDefault();
}
function drag(ev)
{
ev.dataTransfer.setData("Text",ev.target.id);
}
function drop(ev)
{
ev.preventDefault();
var data=ev.dataTransfer.getData("Text");
ev.target.appendChild(document.getElementById(data));
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Drag the W3Schools image into the rectangle:</p>
<div id="div1" ondrop="drop(event)" ondragover="allowDrop(event)"></div>
<br>
<img id="drag1" src="http://i47.tinypic.com/165s8x.jpg" draggable="true" ondragstart="drag(event)" width="336" height="69">
</body>
</html>
and save it .html
WEB SITE WARING MESSAGES
HERE ARE THE CODES:
When a browser requests a service from a web server, an error might occur.
This is a list of HTTP status messages that might be returned:
1xx: Information
Message:Description:
100 Continue The server has received the request headers, and the client should proceed to send the request body
101 Switching Protocols The requester has asked the server to switch protocols
103 Checkpoint Used in the resumable requests proposal to resume aborted PUT or POST requests
2xx: Successful
Message:Description:
200 OK The request is OK (this is the standard response for successful HTTP requests)
201 Created The request has been fulfilled, and a new resource is created
202 Accepted The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed
203 Non-Authoritative Information The request has been successfully processed, but is returning information that may be from another source
204 No Content The request has been successfully processed, but is not returning any content
205 Reset Content The request has been successfully processed, but is not returning any content, and requires that the requester reset the document view
206 Partial Content The server is delivering only part of the resource due to a range header sent by the client
3xx: Redirection
Message:Description:
300 Multiple Choices A link list. The user can select a link and go to that location. Maximum five addresses
301 Moved Permanently The requested page has moved to a new URL
302 Found The requested page has moved temporarily to a new URL
303 See Other The requested page can be found under a different URL
304 Not Modified Indicates the requested page has not been modified since last requested
306 Switch Proxy No longer used
307 Temporary Redirect The requested page has moved temporarily to a new URL
308 Resume Incomplete Used in the resumable requests proposal to resume aborted PUT or POST requests
4xx: Client Error
Message:Description:
400 Bad Request The request cannot be fulfilled due to bad syntax
401 Unauthorized The request was a legal request, but the server is refusing to respond to it. For use when authentication is possible but has failed or not yet been provided
402 Payment Required Reserved for future use
403 Forbidden The request was a legal request, but the server is refusing to respond to it
404 Not Found The requested page could not be found but may be available again in the future
405 Method Not Allowed A request was made of a page using a request method not supported by that page
406 Not Acceptable The server can only generate a response that is not accepted by the client
407 Proxy Authentication Required The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy
408 Request Timeout The server timed out waiting for the request
409 Conflict The request could not be completed because of a conflict in the request
410 Gone The requested page is no longer available
411 Length Required The "Content-Length" is not defined. The server will not accept the request without it
412 Precondition Failed The precondition given in the request evaluated to false by the server
413 Request Entity Too Large The server will not accept the request, because the request entity is too large
414 Request-URI Too Long The server will not accept the request, because the URL is too long. Occurs when you convert a POST request to a GET request with a long query information
415 Unsupported Media Type The server will not accept the request, because the media type is not supported
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable The client has asked for a portion of the file, but the server cannot supply that portion
417 Expectation Failed The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field
5xx: Server Error
Message:Description:
500 Internal Server Error A generic error message, given when no more specific message is suitable
501 Not Implemented The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfill the request
502 Bad Gateway The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server
503 Service Unavailable The server is currently unavailable (overloaded or down)
504 Gateway Timeout The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server
505 HTTP Version Not Supported The server does not support the HTTP protocol version used in the request
511 Network Authentication Required The client needs to authenticate to gain network access
YouTube Video in HTML
TODAY I WILL SHOW TO YOU HOW TO PUT YOUTUBE VIDEOS IN YOUR WEBSITES
HERE THE CODES:
EXAMPLE
Wednesday, December 19, 2012
HOW TO HOST EMEBED FLASHIN HTML
THIS TIME I WILL SHOW TO YOU HOW TO EMEBED SWF IN YOUR WEBSITE:
<body>
<object width="400" height="40"
classid="clsid:d27cdb6e-ae6d-11cf-96b8-444553540000"
codebase="http://fpdownload.macromedia.com/pub/shockwave/cabs/flash/swflash.cab#version=8,0,0,0">
<param name="SRC" value="LINK OF THE SWF">
<embed src="bookmark.swf" width="400" height="40"></embed>
</object>
</body></html>
JAVA SCRIPT IN HTML WRITING
OK THIS IS A LITLE BIT HARD BUT LEARNING FAST IS A COOL THING
The <script> tag is used to define a client-side script, such as a JavaScript.
The <script> element either contains scripting statements or it points to an external script file through the src attribute.
The required type attribute specifies the MIME type of the script.
Common uses for JavaScript are image manipulation, form validation, and dynamic changes of content.
The script below writes Hello World! to the HTML output:
<script>
document.write("Hello World!")
</script>
The <script> tag is used to define a client-side script, such as a JavaScript.
The <script> element either contains scripting statements or it points to an external script file through the src attribute.
The required type attribute specifies the MIME type of the script.
Common uses for JavaScript are image manipulation, form validation, and dynamic changes of content.
The script below writes Hello World! to the HTML output:
document.write("Hello World!")
</script>
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)